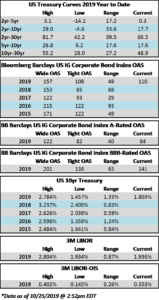
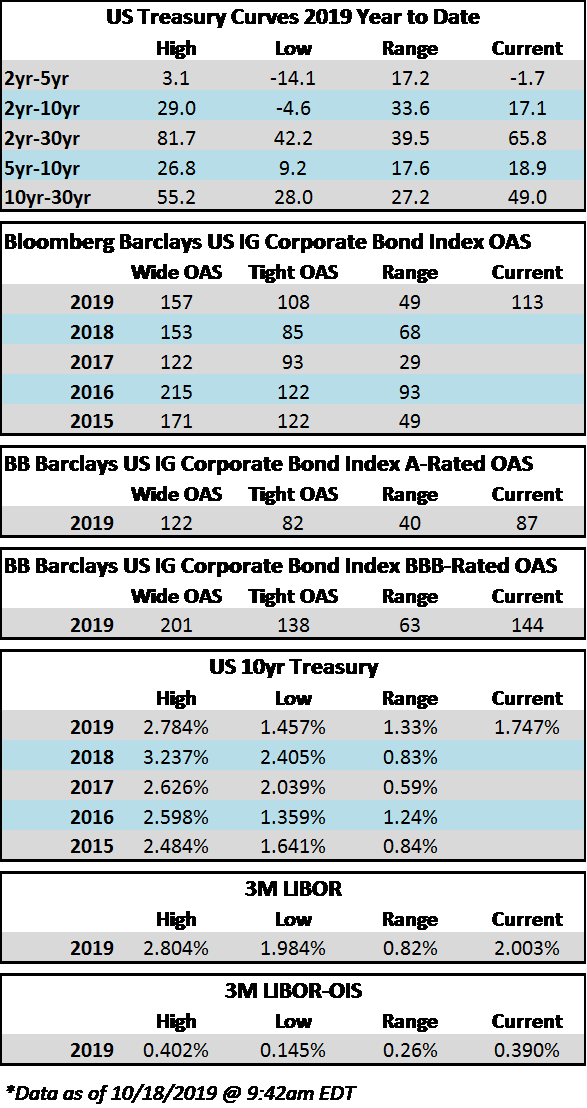
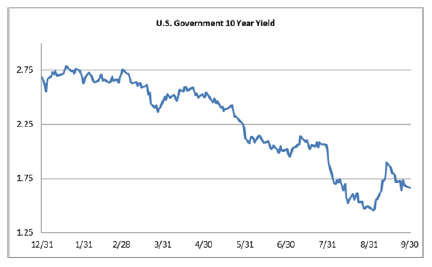
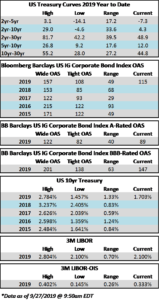
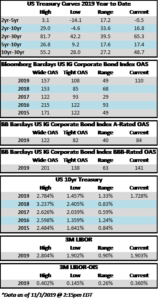
Credit spreads were turbulent during the week. The first half of the week saw tighter spreads, and the OAS on the Corporate Index closed at 106 on Tuesday, the tightest level of 2019. Spreads traded wider from there on the back of Fed commentary on Wednesday which was followed by a surprisingly weak Chicago PMI reading on Thursday morning leading to a close of 110 for the index on Hallows eve. The economic news continued to roll in on Friday morning, but this time it was received in positive fashion as employment numbers beat market expectations. As we go to print amid lighter volumes in corporates most bonds are trading 2-4 tighter which should see the index close right around 108. If we do close at 108 then spreads will have finished the week unchanged. Rates too were volatile during the week with the 10yr closing at 1.84% on Monday but it is now trading at 1.73% on Friday afternoon. This is lower on the week, as the 10yr finished the week prior at 1.79%.
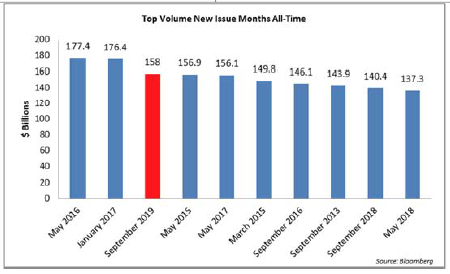
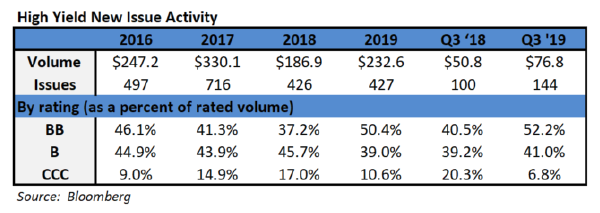
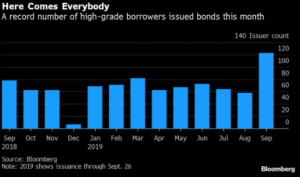
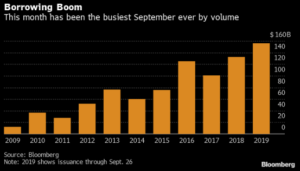
The primary market was somewhat more active this week but finished the month well shy of expectations. October volume closed at $68.6bln versus dealer projections of $85bln according to data compiled by Bloomberg. 2019 issuance stands at $992bln which trails 2018 to the tune of -6%.
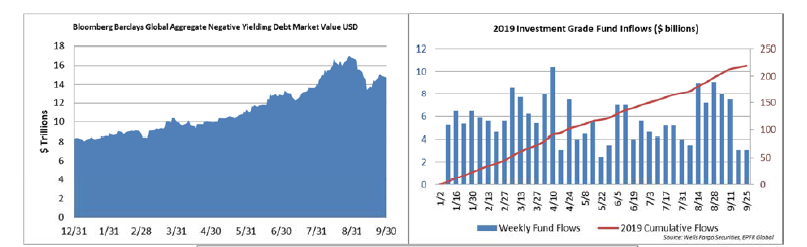
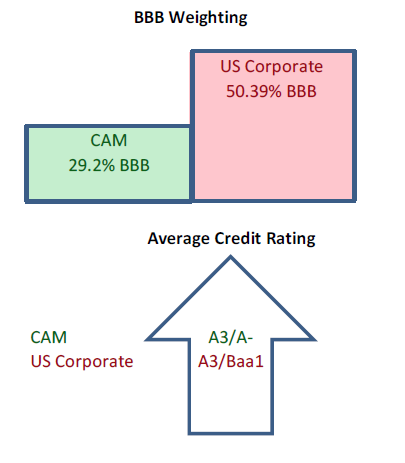
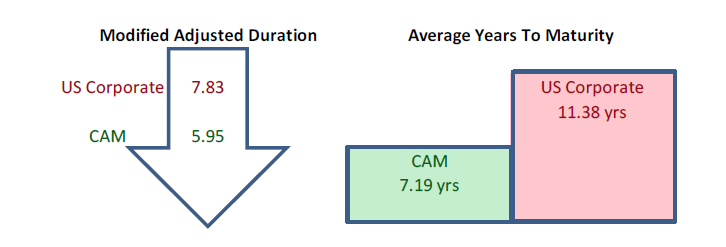
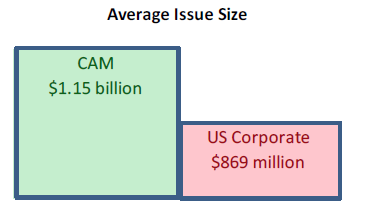
Demand for corporate credit continues to remain robust. According to Wells Fargo, IG fund flows during the week of October 24-30 were +$4.2bln. This brings YTD IG fund flows to +$246bln. 2019 flows are up over 9% relative to 2018.
(Bloomberg) Credit Risk Gauge Drops to Six-Week Low on Bullish Jobs Report
- Investors pushed the cost to protect a basket of investment-grade company debt against default to the lowest level since Sept. 19 following the unexpectedly strong U.S. jobs report on Friday.
- The Market CDX Investment Grade index spread fell as much as 2 bps to touch 52.96 bps Friday morning in New York before paring some of the gains to trade at 53.67 bps at 12:30 p.m, according to ICE Data Services. The index narrowed by the most in almost three weeks, data compiled by Bloomberg show.
- Excess demand for higher-quality bonds and low supply have propelled gains in corporate investment-grade markets. October new IG issues ended at $68.6 billion, falling short of the $85 billion dealer projections by nearly 20%, while cash continues to flow intohigh-grade bond funds.
(Bloomberg) Riskiest Junk Debt Still Isn’t Cheap Enough to Lure Buyers
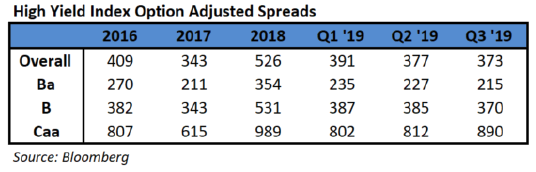
- Notes rated in the CCC tier, essentially the lowest level in the junk bond market, have grown cheaper since May even as most of the market has grown stronger. Risk premiums, or spreads, on the debt are close to their widest level relative to the tier just above them since mid-2016, according to data compiled by Bloomberg.
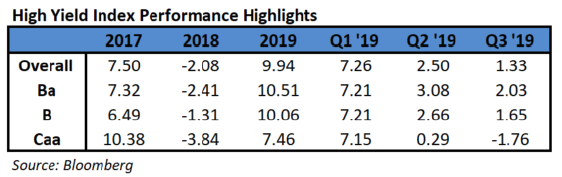
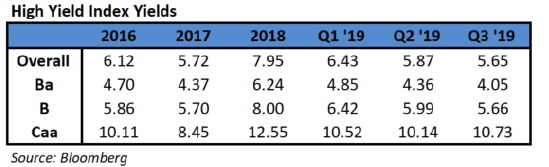
- The weaker performance of the lowest-rated debt underscores how even as investors are reaching for higher returns as the Federal Reserve eases interest rates, they’re still wary of a potential economic downturn and fear that defaults could start to tick higher. The highest tier of junk bonds have gained 13.5% this year, and overall high-yield corporate bonds are up 11.9%, while those rated CCC have gained just 5.7%.
- CCC debt doesn’t usually perform like this. Because the companies that sell the notes are already so close to defaulting, CCC bonds are typically hit harder than the broad market during a market downdraft. When the market recovers, the securities often perform much better. The debt plunged in early 2016 when energy prices dropped, but went on to notch huge returns for the year — 31.5% to the broader market’s 17.1% — as oil prices started recovering.
This year, CCC bonds are performing worse than the market even as the overall supply of the lowest-rated notes has been shrinking. There are about $156 billion of those bonds outstanding today, down from $167 billion in February. So far this year, CCC rated companies have sold around $24 billion of debt, less than the same period for each of the previous two years, according to data compiled by Bloomberg.
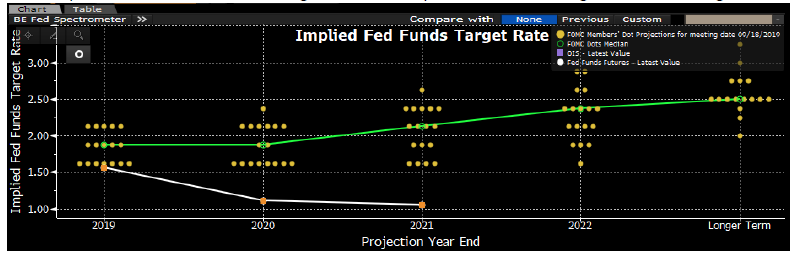
Bloomberg) Top Fed Officials Hammer Home Message That Rates Are on Hold
- Federal Reserve Vice Chairman Richard Clarida reinforced the central bank’s new message this week that interest rates are on hold, saying that both monetary policy and the U.S. economy are “in a good place,” though some risks remain.
- “We have a favorable outlook for the economy,” Clarida said Friday in an interview with Jonathan Ferro and Tom Keene on Bloomberg Television. “We think the economy is in a good place, we think monetary policy is in a good place.”
- He repeated that message in a lunchtime speech at the Japan Society in New York, with Fed Vice Chairman for Supervision Randal Quarles delivering a similar signal at an event at the same time at Yale University in New Haven, Connecticut.
- The vice chairs’ overlapping remarks hewed closely to what Chairman Jerome Powell said earlier this week after the Fed cut rates for a third time this year, signifying a strong consensus at least among the Board of Governors. The Fed has acted to protect a record U.S. economic expansion amid headwinds from trade uncertainty and global weakness, while the domestic economy has been holding up.