Fund Flows & Issuance: According to a Wells Fargo report, flows week to date were -$0.8 billion and year to date flows stand at -$5.6 billion. New issuance for the week was $15.4 billion and year to date issuance is at $129.7 billion.
(Bloomberg) High Yield Market Highlights
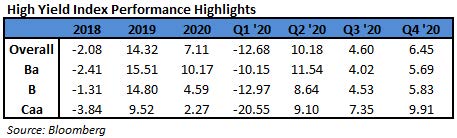
- Year-to-date U.S. junk-bond returns turned negative for the first time since January, and are set to post a weekly loss after Thursday’s 0.29% decline. It was the biggest one-day drop in three weeks, according to data compiled by Bloomberg. This would mark the fifth consecutive week of losses and the longest stretch of weekly declines since August 2013.
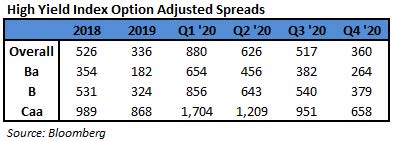
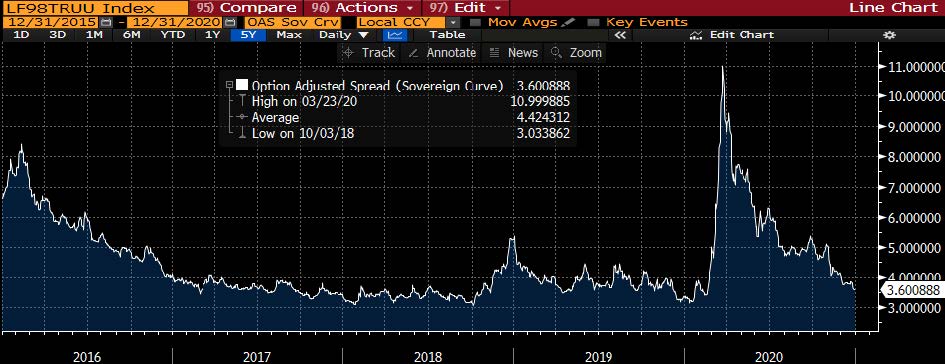
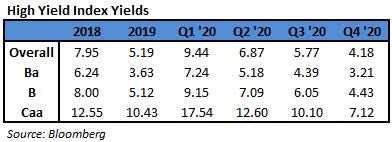
- Yields jumped 13bps to close at a 15-week high of 4.57%, the most in three weeks. Spreads were steady, widening by 5bps to +337 as the 5Y UST rose 6bps to 0.86% on Thursday
- While yields rose, spreads remained intact and “avoided volatility” as the demand backdrop remained supportive despite concerns about retail outflows, Barclays strategist Brad Rogoff wrote on Friday
- “Strong economic growth should allow higher-beta credit to hold its recent outperformance”
- As returns turned negative and investors showed some weariness, there was no serious risk aversion as retailer Neiman Marcus is set to price a $1b offering of five-year notes, rated Caa2/CCC+, as soon as today
- Proceeds of the deal will be used to repay debt it incurred to exit bankruptcy in September
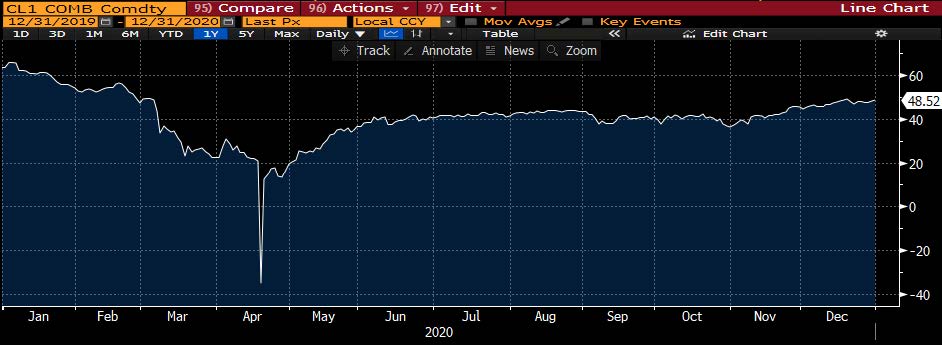
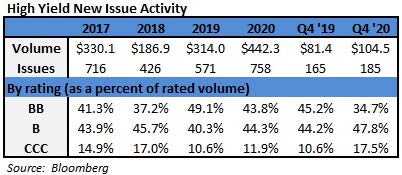
- Junk bonds have come under pressure after pricing more than $40b this month, just about $2b short of making this the busiest March on record. The most active March came in 2017, with $42.165b sold. This year’s first quarter has seen almost $130b of supply, the second-busiest quarter ever
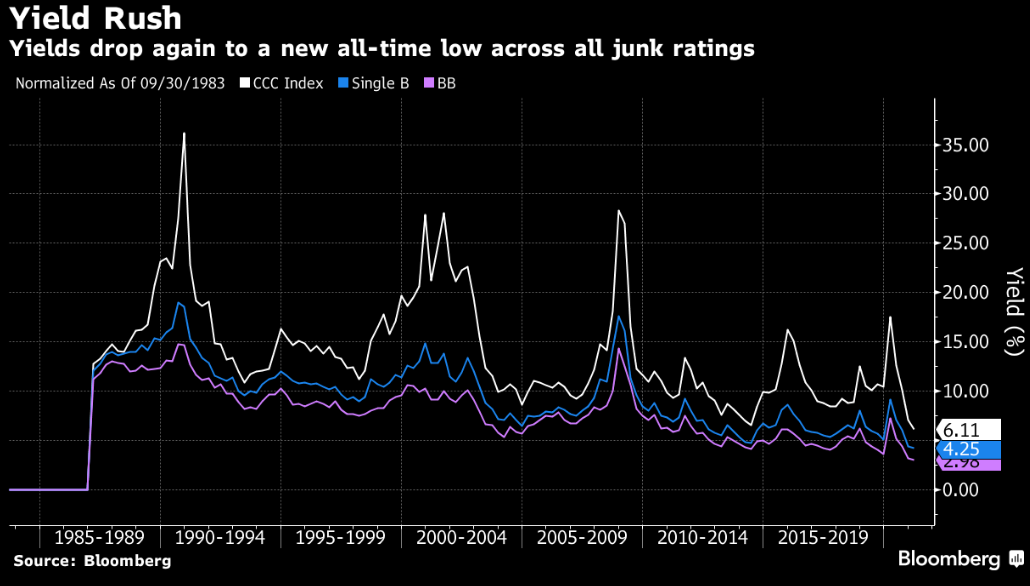
- BB yields rose to a four-month high of 3.72% while spreads held firm widening just 3bps when 5Y UST rose 6bps
- CCCs, the riskiest tier of junk bonds, also posted a loss of 0.2% on Thursday. Yields rose 19bps to 6.76%
- Stock futures rebounded after dropping overnight as the Nasdaq climbed this morning. Oil tried to recover this morning but was heading for the biggest weekly loss since October
(Bloomberg) Powell Faces Tough Campaign to Convince Traders of Fed’s Resolve
- The Federal Reserve succeeded in pushing back against market expectations for a rate hike in the next two years, but only partially.
- The central bank envisages keeping rates near zero to the end of 2023 despite a significantly brighter assessment of growth and higher inflation over the near term. After the release, traders trimmed some of the more-aggressive positioning they’ve been building for a “lift-off” by earlier in 2023.
- But a 25 basis-point hike by the first quarter that year is still reflected in Eurodollar futures, which are priced off Libor and are a decent proxy for future borrowing costs. So traders haven’t exactly brought their views on the timing that much closer to the central bank’s guidance.
- “The market will need to be reminded again and again of the Fed’s commitment” to support the recovery, said Anne Mathias, global rates and currencies strategist at Vanguard Group Inc. “If higher yields don’t slow the economy down, don’t upset the stock market, don’t upset risk-taking, then the Fed doesn’t need to push back hard against them,” she said in an interview.
- Current rates-market pricing reflects a lingering conviction that the pace of the recovery will spur the Fed to action, earlier than it anticipates, though Chair Jerome Powell reiterated Wednesday that the Fed needs to see “substantial further progress” on its employment and inflation goals before thinking about a hike.
- That statement helped short-end rates fall. Seven-year yields remained elevated, however, which suggests positioning for higher interest rates may be building further out the curve. A later rate hike could force the central bank to move faster to tame inflation.
- Market gauges of inflation expectations imply some faith in the central bank’s ability to keep it under control. The five-year breakeven rate, which is derived from the difference between yields on Treasuries and their inflation-protected counterparts, is around the highest since 2008, at 2.63%. That compares with a lower 10-year breakeven rate showing price pressures returning to the Fed’s target over the decade.
- That chimes with the Fed’s guidance, in Mathias’s view.
- “We’re going to see some interim inflation pressure from pent-up spending,” she said. “Net-net, though, the overall secular forces that have kept inflation at bay have not changed.”