CAM Investment Grade Weekly
02/22/2019
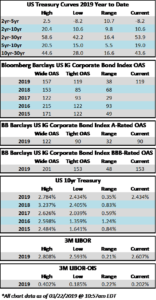
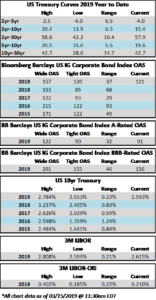
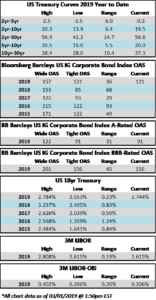
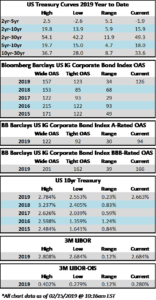
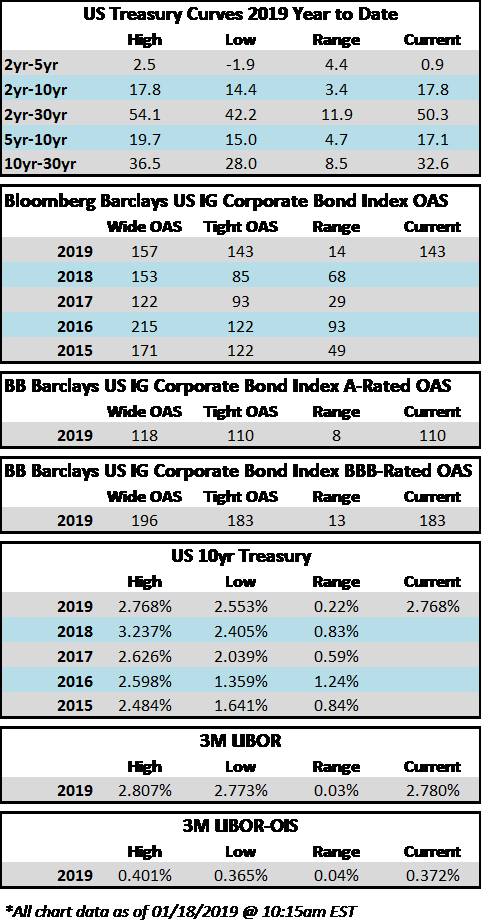
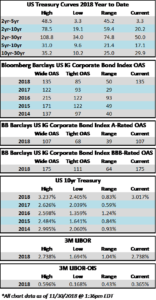
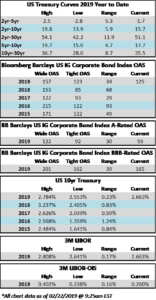
The investment grade credit markets look to end the week on a positive tone, but spreads are largely unchanged for the third consecutive week. The OAS on the index closed at 125 on February 4th and has traded within just a 2 basis point range since then and most of that time was spent within a 1 basis point range. The OAS on the index was 125 at the market close on February 21st and we remain wrapped around that number as we go to print this morning.
It was another solid week of issuance as companies raised over $25bln in new debt during the holiday shortened week. Investor demand for new deals remains very strong and concessions on new debt have continued to grind lower. As far as basis points go, mid-single digit new issue concessions are the name of the game in the current environment. Over $73bln in new bonds has come to market in February and the YTD total is now $178bln.
According to Wells Fargo, IG fund flows during the week of February 14-February 20 were +$1.6 billion. This is a more modest pace of flows compared to prior weeks and it brings YTD IG fund flows to +$30bln. Flows at this point in the year are modestly outpacing 2018 numbers by the tune of 2%.
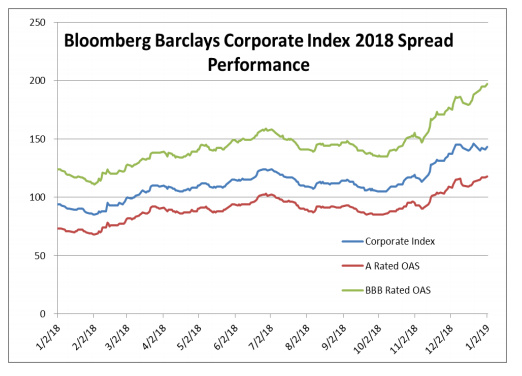
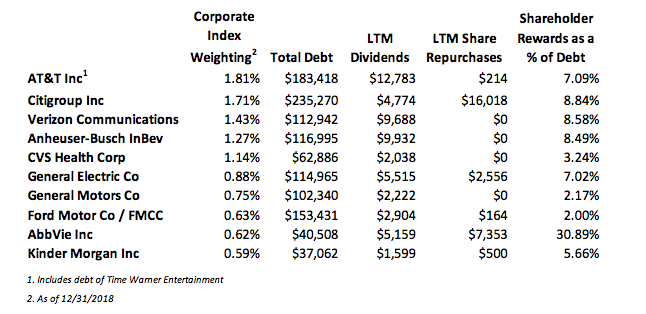
A Blurb about BBB’s – CAM is significantly structurally underweight and quite cautious when it comes to BBB credit. However, we can pick and choose the credits that we would like to own so we are not nearly as worried as some market commentators and those in the financial press seem to be with regard to the growth of the BBB portion of the index. Here are a few interesting recent developments that show that not all the growth in BBB credit should be viewed as negative and that there are some very large BBB-rated issuers who may become A-rated in the near term.
Verizon already has an A- rating at Fitch and it is high-BBB at both Moody’s and S&P so it needs only one of them to upgrade it to single-A before it is “officially” an A-rated credit. An upgrade is a distinct possibility if the company remains on a deleveraging path. Verizon is the second largest BBB-rated bond issuer in the corporate index and an upgrade would result in over $73bln of index eligible debt leaving the BBB-rated portion of the index and entering the A-rated portion.
Bottom line, headlines about BBB-rated credit are just that –to get the real story one must dig into the details.
(Bloomberg) ‘Disastrous’ Kraft Heinz Quarter Foments Street Doubt on M&A
- CAM NOTE: This is yet another example of a highly levered BBB-rated company impairing shareholders in order to pay down debt. It is our view that equity holders are the ones most at risk when it comes to BBB-rated credit, as bond holders have priority in the capital structure waterfall. CAM has no exposure to Kraft Heinz.
- Kraft Heinz Co.’s “disastrous” earnings announcement prompted analysts to question the packaged-food giant’s growth prospects and its capacity to move ahead with plans for a significant acquisition.
- The shares plummeted as much as 28 percent to $34.70. Kraft’s plunge erased about $16 billion in market value. For perspective, that’s more than the entire value of packaged-food peers JM Smucker Co. or Campbell Soup Co.
- Analysts at Goldman Sachs, Barclays, JPMorgan, Stifel, Piper Jaffray, Barclays and UBS cut their ratings on the stock following what Stifel described as a “barrage of bad news:” Quarterly profit missed estimates, the outlook for 2019 was disappointing, and Kraft Heinz cut its dividend, lowered profit-margin expectations and took a $15.4 billion writedown on key brands.
- “The dividend cut and the margin rebase reflect serious balance sheet concerns,” Robert Moskow, an analyst at Credit Suisse AG, wrote in a note detailing his decision to slash his price target to a street-low of $33 from $42. The update “also pokes an enormous hole in management’s contention that it can execute a meaningful acquisition any time soon.”