We hope this commentary finds you all safe and healthy. We wish we would be able to provide you more frequent commentary however things have been changing so rapidly that any update we could provide would have been deemed irrelevant by the time the ink dried on the page. We will seek to provide you with commentary weekly or as is relevant.
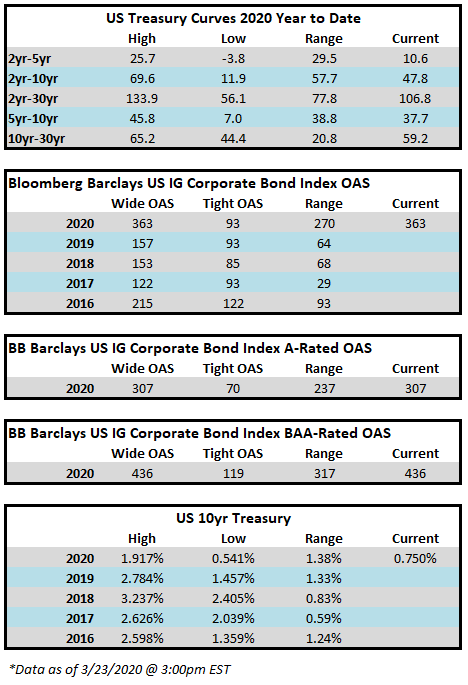
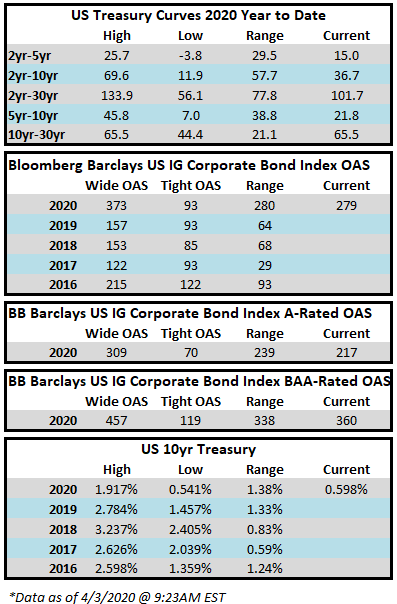
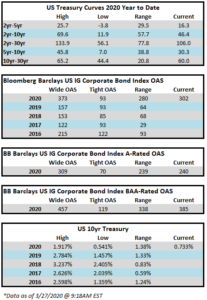
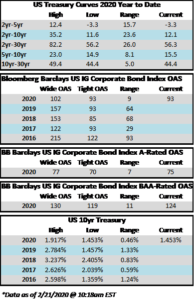
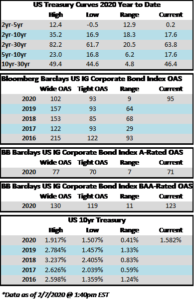
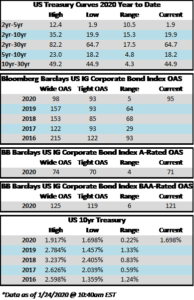
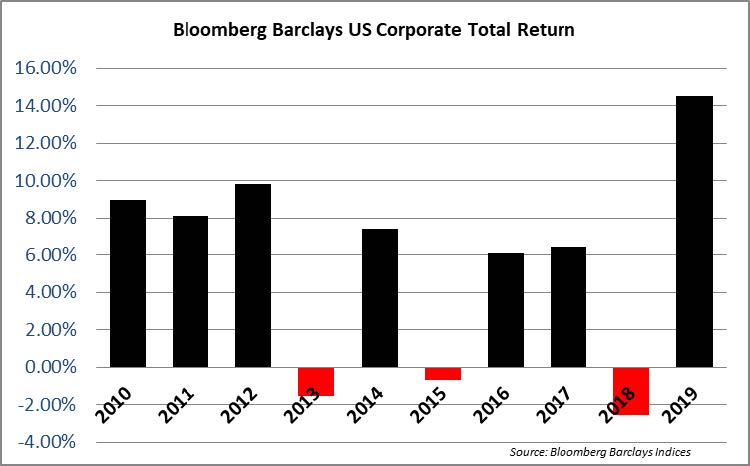
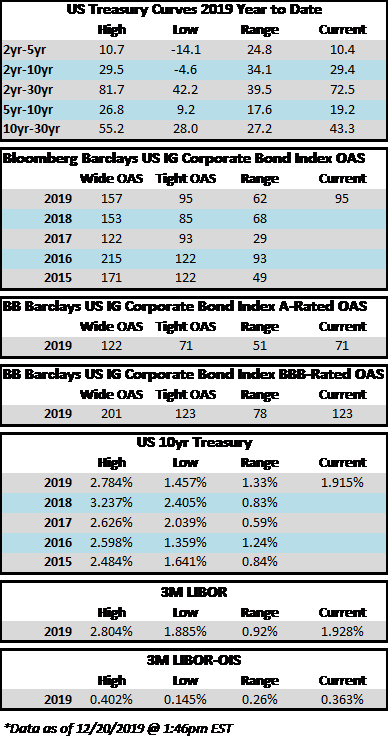
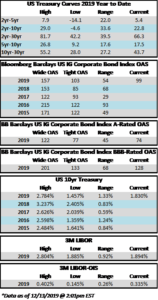
The investment grade credit market has just capped off one of the most volatile two week periods in the history of its existence. The impact of a global pandemic as well as the Saudi-Russia oil standoff has weighed heavily on risk assets of all stripes, and although high quality investment grade typically behaves as a safe haven, even it has not been able to escape the grasp of panicked sellers. Through the week ended March 20, the YTD gross total return on the Bloomberg Barclays US Corporate Index was -10.58%. For context, the S&P 500 was down -28.33% over the same time period. CAM does not provide intra-monthly performance for our portfolios but we are generally more conservatively positioned relative to the corporate index. Recall that CAM has a significant structural underweight on BAA-rated credit by capping our exposure at 30% while the index has a BAA concentration of nearly 50%. CAM also targets a minimum rating of A3 for its portfolio. In a risk off panic, such as the one we have experienced as of late, it is BAA-rated debt that typically underperforms relative to A-rated debt and that has been consistent with what the market has experienced so far in 2020. Year-to-date, A-rated credit has outperformed BAA-rated credit as spreads on the A-rated portion of the index have widened 270 basis points while BAA-rated credit has underperformed to the tune of 46 basis points, having widened 316 basis points thus far in 2020. The AAA/AA portion of the corporate index has held up even better, having outperformed the BAA-rated portion of the index by 126 basis points year to date on a spread basis. To be sure, a pandemic driven global recession is not bullish for investment grade credit, however, it is important to remember that we are talking about high quality investment grade rated companies. This portion of a portfolio is designed to be the ballast that, over time, will reduce volatility and correlations with other asset classes in the context of a well-diversified portfolio. A recession is not good for any asset class and there will be some investment grade companies that are more affected than others. By and large the majority of these companies will see themselves through to the other side and the vast majority of companies will continue to pay interest and debts owed to bondholders. It is also important to remember that, in the framework of a capital structure, bondholders are ahead of equity holders as it is the bondholders that have first claim on the assets of a company. We are already seeing numerous companies change their behavior by suspending share buybacks and cutting dividends in order to protect their balance sheets so that they can continue to make good on their financial obligations that are not negotiable – payments to bondholders.
As far as our portfolio positioning is concerned, we are not infallible and we have some credits that have been impacted by the economic consequences of the pandemic. We are closely monitoring these situations as we always do. We are fortunate in that we have zero exposure to gaming, lodging, leisure or restaurants, as these have been particularly hard hit by the pandemic. We have some exposure to the energy sector but we are materially underweight relative to the corporate index. We have some exposure to airlines but no exposure to unsecured bonds – our only exposure to airlines is through bonds that are secured by the aircraft themselves. Our high quality bias and our bottom up research process leaves us feeling positive about the positioning of our portfolio relative to the index and we are constantly monitoring the portfolio for opportunities to better position, which for us usually means to more conservatively position.
Market Recap
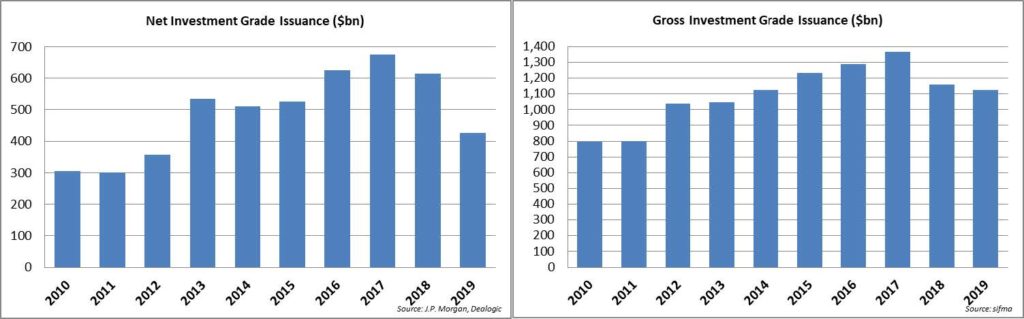
Remarkably, the investment grade primary market remains alive and well as the week of March 16-20 ended up as the third busiest of all time with 23 borrowers bringing over $62bln in new debt. This flurry of issuance was important for the psyche of the market in our view as it once again proved that the investment grade market is never closed to high quality issuers. This was true during the depths of the financial crisis and it is true now. So why, may you ask, would issuers choose to print deals amid such volatility? First, it is really just the prudent thing to do if a company has access – faced with an uncertain near term economic outlook; it makes sense to bolster the balance sheet. Second, due to the drop in Treasuries, debt remains cheap. Take Coca-Cola for example, which was able to issue 10yr debt with a coupon of 3.45% on Friday. That is a very reasonable interest rate when viewed through a historical context. It is also reasonable compensation for investors who are faced with declining yields throughout the world.
Flows have not been the friend for credit investors with long time horizons these past two weeks and the flows themselves have been an even bigger driver of performance than the pandemic in our view. Outflows from IG credit for the week of March 12-18 were an eye-watering -42.7bln according to data compiled by Wells Fargo. This represents the largest outflow on record and is nearly 5x larger than the previous record for a weekly outflow. Investment grade credit is liquid, especially compared to the majority of other fixed income products, such as municipals, but it is not liquid enough to withstand an outflow of this magnitude without serious dislocation, and that is exactly what occurred over the past week. Liquidity for investment grade was easily as bad as it has been since the financial crisis and quite possibly worse based on the opinion of our team at CAM. To be clear, yes the pandemic will weigh on credit metrics for many IG companies, but the underperformance of the IG market over the past week was much more about flows than concerns about creditworthiness. This was panic selling plain and simple. If the market gets to a point where flows are positive or even neutral then the path of least resistance is tighter spreads. The dislocation has created opportunity for committed investment grade buyers especially at the front end of the curve as you can now purchase the 5-6-7 year bonds of some issuers at yields that are greater than their bonds that mature at 10yrs and beyond.
The Federal Reserve continues to act aggressively and decisively as it announced support for numerous market segments on Monday morning. Of particular interest to us is that the Fed will now be buying investment grade rated corporate bonds. The Fed will operate a Primary Market Corporate Credit Facility and a Secondary Market Corporate Support Facility. Through the Primary Facility the Fed will purchase IG rated corporate bonds with maturities of 4 years or less. Through the Secondary Facility, the Fed will purchase IG rated corporate bonds maturing in 5 years or less and it will also be providing liquidity for fixed income ETFs which should go a long way to correcting some of the price discovery problems we saw in the IG market last week. This package by the Fed had the immediate effect of driving IG credit spreads significantly tighter, but more importantly than that it gave the market some much needed confidence. The next step to instilling some semblance of calm into the capital markets would be the passage of a substantial relief package by the Senate. They failed to come to an agreement Sunday evening and for the second time Monday afternoon but we are hopeful that they will come to terms by the end of this week.
As we continue to navigate these turbulent times we wish the best for the health of you and your families. Thank you for your continued interest.
This information is intended solely to report on investment strategies identified by Cincinnati Asset Management. Opinions and estimates offered constitute our judgment and are subject to change without notice, as are statements of financial market trends, which are based on current market conditions. This material is not intended as an offer or solicitation to buy, hold or sell any financial instrument. Fixed income securities may be sensitive to prevailing interest rates. When rates rise the value generally declines. Past performance is not a guarantee of future results. Gross of advisory fee performance does not reflect the deduction of investment advisory fees. Our advisory fees are disclosed in Form ADV Part 2A. Accounts managed through brokerage firm programs usually will include additional fees. Returns are calculated monthly in U.S. dollars and include reinvestment of dividends and interest. The index is unmanaged and does not take into account fees, expenses, and transaction costs. It is shown for comparative purposes and is based on information generally available to the public from sources believed to be reliable. No representation is made to its accuracy or completeness.